During my school years, my fellow geeks and I would eagerly head to the library during break time. One of the most sought-after books was the Guinness Book of World Records. I distinctly remember the entry about the ‘Dead Sea’, which was listed as having the ‘Earth’s lowest elevation on land’. This intriguing piece of information has stuck with me, and now, as an adult, I am excited to write a comprehensive article about the captivating science behind the Dead Sea!
What and Where is the Dead Sea?
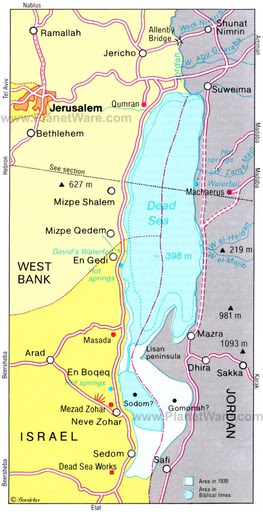
The Dead Sea is a body of water that borders Jordan to the east and Israel and Palestine to the west. It is a remarkable natural wonder, being a hypersaline (extremely salty) lake. The lake’s shores sit at an elevation of 423 m (1388 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land.
What is the reason behind the name “Dead” Sea?
The earliest mention of the Dead Sea can be found in the Book of Genesis, where it is alternatively called the Salt Sea due to its high salt content. With salinity levels close to 35% (342g/kg), it is one of the saltiest lakes on Earth. Additionally, being a landlocked lake with no outflow, the salt is trapped and unable to escape.
During the time of the Romans, it became known as the Dead Sea because it lacked the “normal” forms of life such as fish, plants, and animals. Since then, it has been commonly referred to as the Dead Sea. However, it is also known by other names in different cultures, including the Salt Sea, Plains Sea, Primordial Sea, Sea of Sodom, Sea of Asphalt, and even the Devil’s Sea.
 Credits: Ido Meirovich/Shutterstock
Credits: Ido Meirovich/Shutterstock
The Interesting History of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea is mentioned in the Bible as the “Sea of Plain”. The biblical description is as follows:
“That the waters which came down from above stood and rose up upon a heap very far from the city Adam, that is beside Zaretan: and those that came down toward the Sea of the Plain, even the Salt Sea, failed, and were cut off: and the people passed over right against Jericho”
(Joshua 3:16)
As mentioned earlier, the Dead Sea acquired its name during the Roman era. In that time, salt was highly valued and considered as precious as silver and gold. Salt was even used as currency, and Roman armies were often paid in salt!
Bonus fact: The word salary is derived from the Latin word “sal”, which means to pay remuneration in the form of salt!
Starting with Emperor Trajan, the Romans constructed numerous fortresses near the Dead Sea to protect its valuable salt content. The Dead Sea also served as a luxurious spa for the Roman elite, including King Herod the Great. Cleopatra is also said to have bathed in the Dead Sea due to its supposed therapeutic properties.
Why is the Dead Sea so salty?
As mentioned earlier, the Dead Sea is situated at the lowest point on Earth and is completely landlocked. Many people wonder why it has such high salinity levels.
So, what is the reason behind its saltiness?
Because the Dead Sea is landlocked and at the lowest terrestrial elevation, it becomes the final destination for rain and surface water. However, this water cannot flow anywhere else; it can only evaporate. During the hot summers, there is a significant loss of water (H2O) from the lake through evaporation. Over thousands of years, this has led to a gradual increase in salinity as the water evaporates, leaving behind the salt and other minerals in the Dead Sea.
Does the Dead Sea really lack life forms?
Due to its extremely high salinity level, it is not surprising that the sea and its shores do not have the usual plants and animals that are typically found near a sea. However, with the advancement of science and technology, researchers have discovered that the Dead Sea is not actually “dead” and devoid of all life. Several studies have confirmed the existence of colonies of tiny microbes in the Dead Sea. One of the most well-known organisms is the Dunaliella algae, which is believed to provide various health benefits. The Dunaliella algae have a high concentration of beta-carotene, antioxidants, and certain vitamins. In addition to microbes, other animals such as swamp cats, storks, marsh frogs, and snails are occasionally spotted near the shores of the Dead Sea.
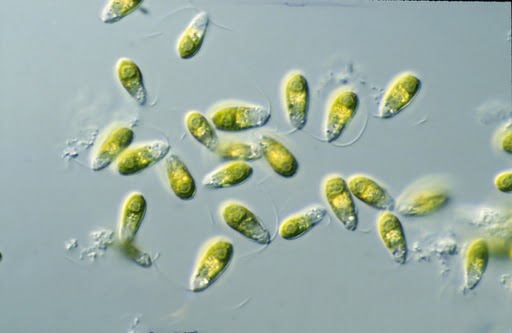 Dunaliella algae: a microbe that can survive in the harsh, saline waters of the Dead Sea
Dunaliella algae: a microbe that can survive in the harsh, saline waters of the Dead Sea
What Causes You to Float in the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea is a popular tourist destination because of its unique characteristic: you can float in the sea even if you cannot swim! Unlike other bodies of water, swimming is not possible in the Dead Sea, you simply float.
For those who have never been to the Dead Sea, you may be curious about the sensation of being in it. Once you enter the water, you will feel as though the water is pushing you up from the bottom, allowing you to float on the surface. As you move further away from the shore, your body will feel lighter and more buoyant.
 Credits: ProfStocker/Shutterstock
Credits: ProfStocker/Shutterstock
Now, the question arises: why do you naturally float in the Dead Sea instead of sinking? The answer lies in the water’s “high salinity.” With over 340 grams per kilogram of salt, along with a high concentration of other minerals, the water in the Dead Sea is denser than other bodies of water. It is even denser than the average human body. Therefore, when we enter the Dead Sea, our bodies remain afloat due to our ‘relatively’ lower density compared to the surrounding water.
 Dead Sea Therapy (Credits:Anton Kudelin /Shutterstock)
Dead Sea Therapy (Credits:Anton Kudelin /Shutterstock)
The high salinity also means that you cannot “dive” or “swim” in the water. You will simply float. It is also advised to avoid submerging your head in the water, especially your eyes. Additionally, individuals with open wounds or cuts should refrain from entering the Dead Sea, as the exceptionally high salt content could irritate those wounds.
